
The “admin-gui” role allows the user to access the /host-manager/html URL and create, delete, and otherwise manage virtual hosts. In this example, we’ll create a user with “admin-gui” and “manager-gui” roles.
Apache tomcat download how to#
This file is a template with comments and examples showing how to create a user or role.
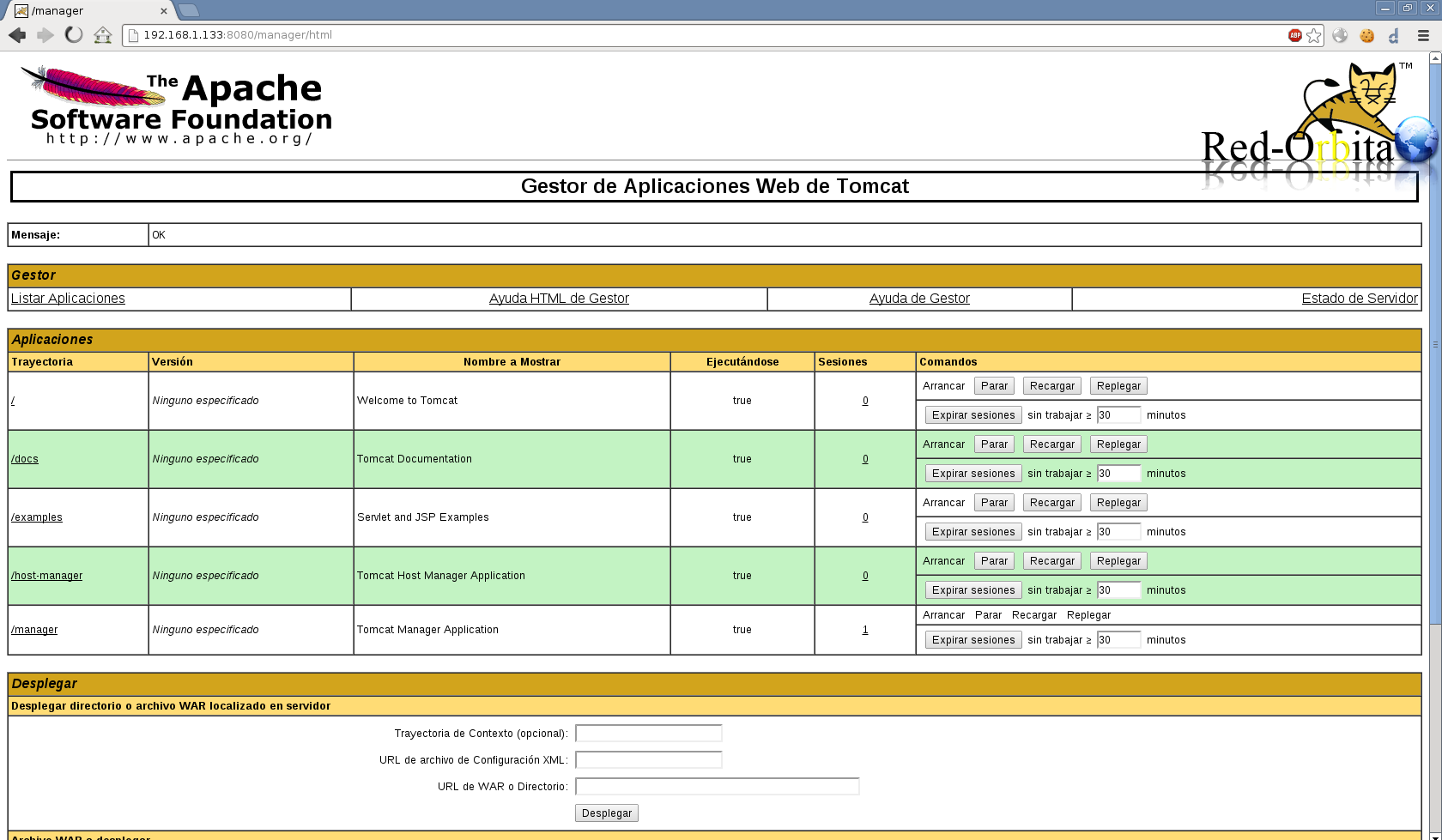
Tomcat users and roles are defined in the tomcat-users.xml file. The web management interface is not accessible because we have not created a user yet. Configuring Tomcat Web Management Interface #Īt this point, you should be able to access Tomcat with a web browser on port 8080. It’s a best practice to allow access to port 8080 only from your internal network. Generally, when running Tomcat in a production environment, you should use a load balancer or reverse proxy Use the following command to open the necessary port: sudo ufw allow 8080/tcp If your server is protected by a firewallĪnd you want to access Tomcat from the outside of your local network, you need to open port 8080. You can start, stop and restart Tomcat same as any other systemd service: sudo systemctl start tomcat sudo systemctl stop tomcat sudo systemctl restart tomcat Configuring Firewall # Process: 5342 ExecStart=/opt/tomcat/latest/bin/startup.sh (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/rvice enabled vendor preset: enabled)Īctive: active (running) since Mon 17:58:37 UTC 4s ago The output should show that the Tomcat server is enabled and running: Save and close the file and notify systemd that a new unit file exists: sudo systemctl daemon-reloadĮnable and start the Tomcat service: sudo systemctl enable -now tomcatĬheck the service status: sudo systemctl status tomcat Modify the JAVA_HOME variable if the path to your Java installation is different. Instead of using the shell scripts to start and stop the Tomcat server, we’ll set it to run as a service.Īnd create a rvice unit file in the /etc/systemd/system/ directory: sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/rvice These scripts are used to start, stop and, otherwise manage the Tomcat instance. : sudo sh -c 'chmod +x /opt/tomcat/latest/bin/*.sh' The shell scripts inside the Tomcat’s bin directory must be executable To user and group tomcat: sudo chown -R tomcat: /opt/tomcat The system user that was previously created must have access to the tomcat installation directory. Later, when upgrading Tomcat, unpack the newer version and change the symlink to point to it.
Apache tomcat download zip file#
To download the Tomcat zip file to the /tmp directory: VERSION=9.0.35 wget $ /opt/tomcat/latest Before continuing with the next step, check the Tomcat 9 download page to see if a newer version is available. Tomcat binary distribution is available for download from the Tomcat downloads pageĪt the time of writing, the latest Tomcat version is 9.0.35. To do so, enter the following command: sudo useradd -m -U -d /opt/tomcat -s /bin/false tomcat Downloading Tomcat # We’ll create a new system userĪnd group with home directory /opt/tomcat that will run the Tomcat service.
Running Tomcat under the root user is a security risk. OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 11.0.7+10-post-Ubuntu-3ubuntu1, mixed mode, sharing) OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 11.0.7+10-post-Ubuntu-3ubuntu1) The output should look something like this: openjdk version "11.0.7"

Once the installation is complete, verify it by checking the Java version: java -version
Apache tomcat download install#
Or root to update the packages index and install the OpenJDK 11 JDK package: sudo apt update sudo apt install openjdk-11-jdk Run the following commands as root or user with sudo privileges , the open-source implementation of the Java Platform. Tomcat 9 requires Java SE 8 or later to be installed on the system. Tomcat is lightweight, easy to use, and has a robust ecosystem of add-ons. It is one of the most popular choices for building Java-based websites and applications. This tutorial describes how to install and configure Tomcat 9 on Ubuntu 20.04.Īpache Tomcat is an open-source web server and Java servlet container.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
